Establishing Renewable energy zones in Australia is one step towards Australia's clean energy network. Wind farms, solar panels and batteries are converging to provide electricity to houses anywhere. Shutting down coal plants, REZs are providing cheap energy and local employment to rural towns. In today's world, billions of dollars are developing societies by establishing employment plans.
What are Renewable energy zones?
Definition and Purpose
Renewable energy zones refer to designated locations for coordinated renewable energy development. This is in addition to being areas where clean energy renewable projects synchronize amongst themselves. The states and the Australian Energy Market Operator control the REZs in a bid to enhance sustainable power generation. Unlike individual connections in each project, REZs are shared communally. The shared approach lowers the cost of erecting electricity lines and equipment.
Major Characteristics
Every region of renewable energy needs five important things to operate. The units successfully provide clean electricity to houses:
- Solar panels and windmills generate green electricity every other day.
- More energy is stored in a battery or as water, so it can be used the next time.
- They provide electricity to the national grid, focusing on coordinated, reliable supply.
- The connection points connect projects to the grid in the best possible way.
- Site selection relies on high irradiation or high wind.
How REZs Fit Into Energy Plans
The renewable energy zones enable the Australians to achieve the clean energy targets. Since coal power plants will be closed by the 2030s, the needed energy will be supplied by REZs. New South Wales, for example, plans to achieve the net zero emissions by 2050. For this reason, the nation will feature a consistent supply of electricity in the state of transition with the help of REZs.
Where Are REZs Located?
State-by-State Summary
New South Wales is also leading the way. It stands out with five Renewable energy zones that generate energy on a very grand scale. They will provide more than 12 gigawatts of power. The other states also are creating zones:
- Victoria will have six zones in its regions.
- Queensland will have twelve zones, which will be distributed in three regions.
- South Australia forms a section of the National Electricity Market as well as hosts key renewable projects. However, it doesn’t have a specific number of officially designated zones of renewable energy.
Big REZs to Watch
The first to be approved in Australia is Central West Orana and it began in November 2021. It's looking for 4.5 gigawatts of power near Dubbo and Dunedoo. Also, it anticipates investments of up to 25 billion dollars. This will come with job creation at thousands levels.
Hunter Central Coast transforms the existing power networks to be efficient. Ausgrid envisions 1 gigawatt across nine councils. The construction work started in 2025, and initial capacity is expected by early 2026. However, full completion is projected for 2028.
Transmission Infrastructure
The renewable energy zones are connected to the national electricity grid by high-level powerlines. They have the sole purpose of transporting the clean energy:
Project EnergyConnect provides a link of more than 900 kilometers. This is between NSW and South Australia.
- HumeLink performs well in southern NSW's Snowy 2.0.
- VNI West improves Victorians' and NSW's connectivity.
- The New England REZ features an intended network capacity of 8 gigawatts. This is going to be delivered in stages ( 3.6 GW by 2034 & 2.4 GW by 2032).
REZ Zone Summary
| Zone Name | State | Status | Target (GW) | Timeline |
| Central West Orana | NSW | Under Construction | 4.5 ( for stage 1), 6.0 by 2038 | Late 2020s( for stage 1 by 2030) |
| New England | NSW | Planning phase | 8.0 ( 2.4 GW for Stage 1 and the remaining 3.6 GW for stage 2) | Stage 1 by 2032 and stage 2 by 2034 |
| Hunter Central Coast | NSW | Planning approved on Sep 2025 | 1.0 | 2028 |
| South West NSW | NSW | Access rights awarded | 2.5 ( Initially), again awarded 3.56 GW | Late 2020s or by 2030 |
Benefits of Renewable Energy Zones
Saving Money Via Teamwork
Renewable energy zones help share energy between projects, resulting in savings. A good case is when ten wind farm projects depend on a single connection. Here, the cost goes down substantially. EnergyCo estimates that REZs are fundamental to reducing connection costs. They do so by 30% to 40%. Lower project costs are important for everyone because they lower their electricity bill.
Keeping the Grid Strong
REZ's battery systems are important. They are a section of the wider strategy to coordinate renewable production as well as transmission infrastructure. Planning strategically is also important for the ability to deliver reliable power. This is usually from the different types of renewable generation.
- Coastal wind farms can continue to generate energy to keep homes powered at night.
- Inland solar is pivotal for generating energy during the day when it is needed.
- Batteries help to smooth the balancing of energy needs through the day.
- Water storage helps to manage longer duration energy backup needs.
Boosting Local Economies
Renewable energy zones provide a significant economic opportunity for rural areas of Australia. There's one thing to note according to the NSW government. It says, across the five zones, we are expecting over $32 billion in investment. These investments will lead to the creation of jobs. That's 2800 permanent jobs and construction jobs, 6300 in number.
There will be significant demands for services from the construction workers. That's another positive spin off for local businesses.
- Restaurants as well as hotels provide services to employees on a routine basis.
- Local businesses ensure that work proceeds smoothly by delivering equipment and supplies.
- Renting equipment and transport provides a consistent stream of income.
- Hospitality and retail record enormous growth with the increase of local spending cases.
Other farmers reap large lease payments. This is by leasing space for turbines or power lines. This revenue is instrumental. That's especially in changing the rural economies as time goes on.
Challenges and Concerns

Land and Environmental Issues
Massive renewable projects do raise environmental concerns. That's apart from land-related concerns. Each developer of these projects needs to do one thing. That's to address these concerns very carefully.
- Solar land may take away from productive farmland, reducing the crop yield.
- Wind turbines affect the view of the landscape to an even greater extent.
- Projects can affect migration patterns or endangered species.
- Construction-related projects need to protect Aboriginal cultural places.
- Having several projects in one place increase the potential impact.
Each developer makes an effort to protect cultural heritage or wildlife. They do that by meeting with strict regulations. Also, they involve Traditional Owners in the planning process.
Community Support and Engagement
Robust community support is a fundamental advantage for successful REZs. It helps avoid conflict with the local communities. Plan on legal issues or suits about delays if you ignore that. This is especially where the local community concerns have been ignored. Other farmers may not raise issues. But, the neighboring landowners may feel they are taking on the environmental burdens. Therefore states require that the developer has way to demonstrate effective community engagement.
Power Line Issues
A large portion of REZs do not have enough power line capacity to connect with new projects. New power lines are expensive and time consuming to build:
- Full approval can take as little as 18 months up to 36 months.
- Land access negotiations are challenging, especially access through buildings.
- Projects that are some distance from lines incur significant cost to connect.
- The grid may also require additional equipment to stay stable.
How REZs Are Planned and Managed
The Integrated System Plan
The Australian Energy Market operator reviews and rewrites its Integrated System Plan every 2 years. Besides exploring possible scenarios, this plan also maps out upcoming energy requirements. States rely on the plan as a framework, from which they create their unique REZ planning strategies. Through the plan, it becomes easy for the regions to coordinate transmission related investments. However, each state determines its top-priority zones on its own or independently.
State Responsibility
Each state has agency that oversees and integrates its REZ for optimal success. For example, the EnergyCo is a good case in NSW. It oversees all approvals, lines and communication with the community. VicGrid does similar work in Victoria. Queensland has plans for 8 spots in three primary areas.
Guidelines and Procedures
The Electricity Infrastructure Investment Act 2020 (NSW) is crucial. It provides the framework for renewable energy zones (REZ). Developers submit tenders to connect in REZs. The project that wins the tender is provided with a right to connect. This is without disconnection issues:
- The evaluation includes factors such as costs, readiness, and community benefit.
- Contracts over the long-haul will support income sustainability for developers.
Progress and Case Studies
Hunter Central Coast REZ updates
In Dec 2024, Ausgrid recorded a major update. It was confirmed as the network operator for Hunter Central Coast. The REZ will focus on upgrading existing powerlines. This is to expand capacity rather than developing new lines. Hunter Central Coast REZ encompasses 9 local government areas. Also, in April 2025, a Review of Environmental Factors (REF) was released by Ausgrid for public exhibition as well as comment.
Central West Orana REZ Updates
Central West Orana, Australia's first REZ, moved quickly this past year. This was after approval in November 2021. TeranGrid worked with communities in planning the power line routes in 2022. In mid-2025, construction of the transmission infrastructure began and is expected to be up and running by 2028. The zone is estimated to produce 4.5 gigawatts. The transmission infrastructure has an approximate cost of $5.5 billion. Additionally, REZ is expected to attract private investment into the region of up to $25 billion.
Case Study REZ Timelines
| Zone | Approval | Construction | Operational | Capacity |
| Central West Orana | Nov 2021 | Mid-2025 | Late 2028 | 4.5 GW |
| Hunter Central Coast | Dec 2022 | 2024-2025 | 2030 | 1.0 GW |
| New England | Approved | TBD | Early 2030s | 8.0 GW |
Impacts on Consumers, Investors, and Communities
Impacts on Electricity Bills
Renewable energy zones are crucial. They support downward pressure on the wholesale price of electricity, over time. Increased competition between generators lowers costs to consumers. For example, NSW estimates households may save a little above $130 per year. Homeowners with solar PV and batteries would benefit most. This is from a stronger electricity grid.
Developer Opportunities
REZs provide significant opportunities to develop wind, solar, and battery firms. Developers must complete several key tasks:

- Land use agreements with landowners to start a project.
- Accurate approval and funding plans.
- Strong community engagement and local job hire.
- Technical and studies that support the implementation of the project.
Long term power agreement to allow developers to access funding.
Community Benefits
Every major REZ share community benefits with local communities. Community benefits are designed to significantly boost the local area:
- Funding for community projects - parks, schools.
- Internet and mobile upgrades and other communications services.
- Stronger power lines for reliable delivery.
- Local job hirings and training programs.
- Payments to local farmers to host a turbine or power line.
Powering Homes with BLUETTI
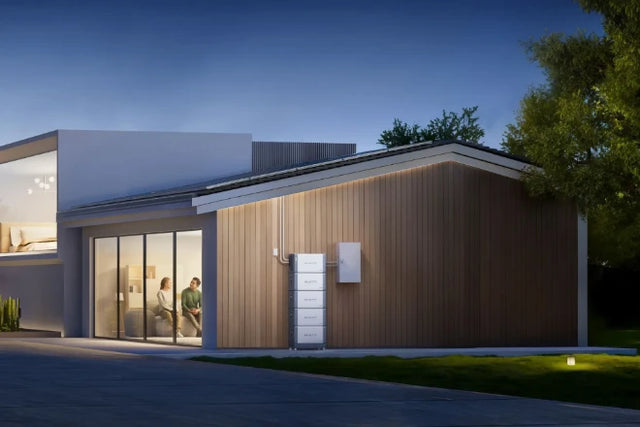
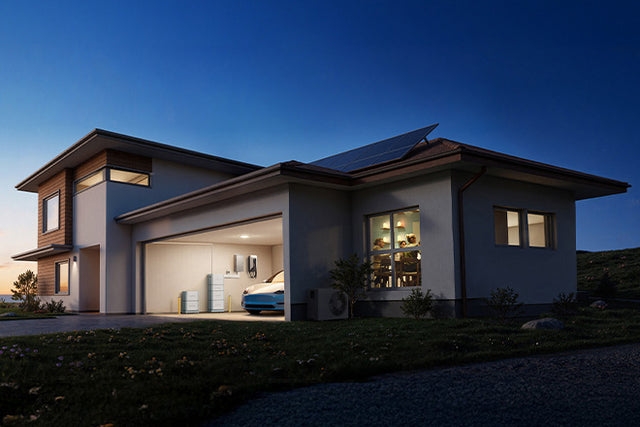
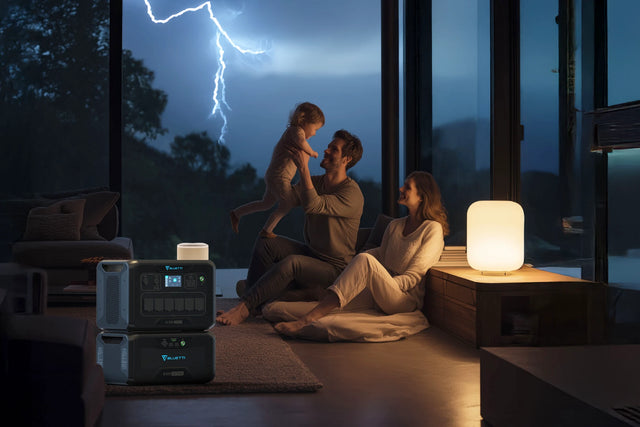
EP760 - Home Energy Storage
The BLUETTI EP760 allows Australians homes to use clean energy every day. It is best when combined with rooftop solar panels that can provide up to 80% energy independence. The system starts with 4.96 kilowatts of energy storage. This can be increased to 19.84 kilowatts by adding up to 4 batteries.
The BLUETTI can provide up to 7.6 kilowatts. This can run air conditioners or appliances. There is also a smart app. This gives real-time monitoring for energy usage and energy storage level.
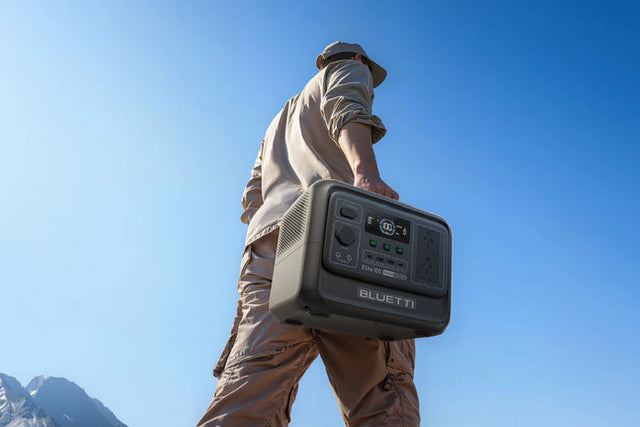
Apex 300 - Portable Power
The BLUETTI Apex 300 is excellent for off-grid or emergency applications. It stands out with 2,764.8 watt-hours of usable power and 3,840 watts of continuous power. Additionally, it has the ability to power 7,680-watt surges for fridges or power tools. Plus, you can plug in multiple units for even more power. Thus, this is amazing for camping or RV trips, working on a construction site, or charging a GPS, camera, or radio.

What Next for REZs?
Expected Development
Australia will require 50 to 550 gigawatts of new clean energy capacity by the year 2050. This depends on adoption and use of electric vehicles and hydrogen exports. Most of this new capacity will use proposed REZs. REZs will host most of this clean energy. The 2020's focus is on implementing REZs in locations like Central West Orana. By 2040 it will be practical to develop REZs in remote locations.
Storage & New Tech
The next generation of REZs will also include batteries and storage facilities. A combination of wind and solar with battery storage provides better value for money:
- Batteries help to eliminate any wasted power generated, and they help to stabilise the grid.
- Water storage can be used to time shifting energy to when it is most required.
- Hydrogen generation could also add that flexible energy usage.
Regarding battery costs, they have decreased in costs as much as 90% over the last decade.
Regulatory Improvements
The actual result of the fast approvals is that the development of REZ may be rather expedited. Now the quality of approvals is approximately 18 to 36 months per project. Even the governments are planning zone-wide approvals in order to accelerate the same. They are trying to do one thing with this measure. This is to balance between the need of clean energy and nature conservation. They are doing this while at the same time being careful.
Conclusion and Key Points
Why REZs Matter for Clean Energy
The clean energy transition of Australia focuses on renewable energy zones. They are replacing coal plants. The government incentives, & personal funds are essential to success. This also includes the involvement of local stakeholders. REZs spur local economies and reduce emissions in an efficient manner.
What Can Stakeholders Do
To successfully develop projects by REZ developers, the governments should have clear rules. It should also begin to fund power lines to REZs. Besides that, developers must engage communities. They must additionally observe high-quality environmental standards. Communities deserve clear information, consultations of projects, not forgetting fair payments.
Questions for Citizens
The following are some of the pivotal questions. They are the ones to ask regarding the establishment of REZ and its implications:
- Does the environmental regulations and directives have proper compliance during building projects?
- Who controls the community benefit funds and their budget allocations?
- What are the ways in which developers guarantee jobs and infrastructure promised?
- Does the development of REZs balance energy demand and nature?
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the ways in which renewable energy zones save on costs of energy?
They accomplish this by lowering the wholesale prices. Shared transmission decreases costs incurred when it comes to developers per megawatt connection. Once it is operational, the charges of this type of energy generation become cheap. Network charges fix up expenses of new transmission infrastructure, however. Increment of savings happen over a lengthy period of time.
- Do communities invest in REZ projects?
A significant percentage of these projects is sponsored by large energy firms. Some of the community energy societies explore local funds. A few of those are successful. Listed developers provide an avenue for indirect involvement through shares. Community benefit schemes are yet another kind of investment accruing benefits.
- What happens when those projects have been over?
All developers are obligated to the decommissioning of lease agreements. The developers are supposed to remove equipment and rehabilitate the land after that. Even in the case of the collapses of companies, this would be guaranteed by financial securities. The transmission part of it may be permanently handed over to the network owners. Here, rehabilitation standards are very important. They guarantee the landholders are offered with property that is within acceptable conditions.
- Do REZs impact property values?
Host properties receive lease income. Short term effects may affect neighbors living near the site. This happens mostly when a construction work is being carried out. These tend to recuperate following successive completion of the construction phases. Distant properties quantify some little or no value effect.
- Do REZs contain gas, or nuclear?
No. Currently, nuclear is not allowed in the Australian federal legislation. It is also not associated with the gas production. Zones are also striving to provide zero emission power. This is in place of coal.











































































![[Phased Out] BLUETTI B80P Expansion Battery | 806Wh](http://www.bluettipower.com.au/cdn/shop/files/202310025B80P_2000-2000px_4_4caa0c1c-4dab-4272-9e9b-2b7507e5bd81.jpg?v=1713777870&width=200)
![[Phased Out] BLUETTI B210P Expansion Battery | 2,150Wh](http://www.bluettipower.com.au/cdn/shop/files/2_08cf9ef3-03a4-4489-b641-d3edb8094896.webp?v=1716016566&width=200)






















































































































![[Phased Out] BLUETTI B80P Expansion Battery | 806Wh](http://www.bluettipower.com.au/cdn/shop/files/202310025B80P_2000-2000px_4_4caa0c1c-4dab-4272-9e9b-2b7507e5bd81.jpg?v=1713777870&width=120)
![[Phased Out] BLUETTI B210P Expansion Battery | 2,150Wh](http://www.bluettipower.com.au/cdn/shop/files/2_08cf9ef3-03a4-4489-b641-d3edb8094896.webp?v=1716016566&width=120)