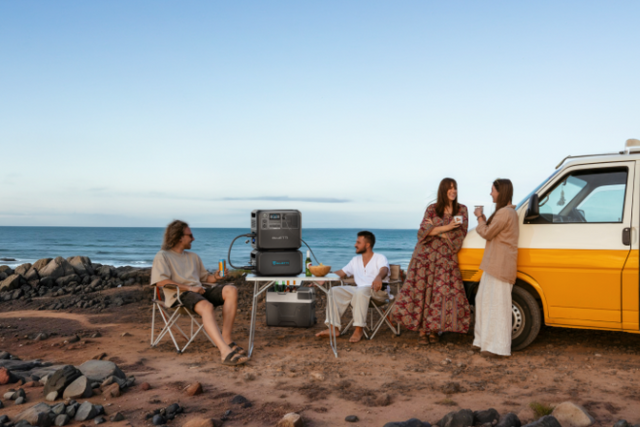
Are you on the hunt for a reliable power source for your electronics or appliances? If yes, then a DC power supply is your best bet. This device assists you in converting AC current to direct current, which gives a more stable voltage for almost all of your devices. Let’s comprehensively learn about a DC Power Supply.

Types of DC Power Supplies
The Linear Power Supplies
A linear power supply allows you to convert your AC power supply into a DC supply by using a transformer and voltage regulator — this allows you to have a stable and low-noise output. However, compared to other similar tools, linear power supplies are less efficient and are only ideal for sensitive devices like audio equipment, laboratory instruments, etc.

Switched-Mode Power Supplies
An SMPS uses high-frequency switch technology which allows it to change your AC current to DC more easily and efficiently. At the same time, it is also highly energy-efficient and comes in a really compact size which also aids it in creating less heat. This alone makes it an ideal tool for your devices like computers, telecommunications, LED lights, etc all of which require a reliable and lightweight power solution.

Safety Standards and Regulations
Electrical Safety Standards
If you are investing in an AC DC power supply make sure that it obeys the specific electrical safety regulations for a safe operation. This is a mandatory process that makes sure that all of the electronic devices like your DC power supply comply with the Australian electrical safety outlines.
Residual-Current Devices
More commonly known as safety switches, these devices are crucial for protecting you against any electrical faults by quickly cutting off the power supply when there is a fault. Moreover, in Australia, using these RCDs is mandatory in different settings to prevent any electrical shock incidents and further increase electrical safety.
Differences between DC and AC power supplies
The main difference between AC DC power supplies is that AC power supplies change direction every now and then while DC power supplies deliver a steady voltage, which also makes it ideal for batteries as well as low-voltage applications.
Why AC is primarily used in Australian homes instead of DC
Almost all Australian homes use AC power because it can effectively travel long distances with little to no energy loss compared to DC. This is also a big reason why most households in Australia need a DC power supplier for their DC-powered devices.
Common AC and DC Appliances in Australian Homes
Common AC Appliances
-
Refrigerators
-
Air conditioners
-
Washing machines
-
Dishwashers
-
Electric ovens
-
Microwave ovens
-
Television sets
Common DC Appliances
-
LED Lighting
-
Car Fridges
-
Laptops and Computers
-
Solar Battery Storage Systems
-
Smartphones, Tablets
-
Rechargeable batteries

How to Choose a DC Power Supply
When choosing a DC power supply for home electronics, portable devices, or off-the-grid energy storage, consider the following:
-
Matches Voltage and Current – This ensures safe use and avoids damaging devices, including laptops, LED lighting, and rechargeable batteries.
-
Efficiency – Minimizes energy loss, which is important for solar battery storage and prolonging the life of batteries in mobile power systems.
-
Portability – A small and lightweight design is helpful for trips, camping, and other applications where portability is crucial.
-
Protection Features – Protects against voltage spikes, surges, and short circuits to avoid damaging your valuables like smartphones and tablets.
The Limitations of DC Power Supplies
Although DC power is extensively used in small electronic devices, it has some disadvantages when it comes to upscaling:
-
Limited Compatibility – Most common household appliances, such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and microwaves, require AC power and cannot be used directly from DC power.
-
Transmission Losses – DC power is not very efficient over long distances and therefore cannot be used for home-wide power distribution systems.
-
High Current Demand – Large-scale DC systems are complicated and costly as they require heavy wiring and sophisticated power control.
-
Inverter Requirement – Some AC appliances require a DC to AC inverter to run, which lowers efficiency and increases system complexity.
Why the BLUETTI AC200L is a Smarter Alternative
The BLUETTI AC200L is designed to address the limitations of conventional DC power supplies by facilitating:
-
Dual AC and DC Outputs – Provides power to DC-enabled devices such as laptops and standard AC devices, including microwaves, without the need for converters.
-
High Capacity (2,048Wh) – Lasts for more time, suitable for both domestic backup and outdoor activities.
-
Portable Design – Designed for ease of transportation, ideal for use when camping, on road trips, or for remote work.
-
Expandable Battery – Enables expansion of battery capacity for future usage as energy requirements increase – perfect for off-grid applications.
-
Multiple Charging Methods – Can be recharged by solar panels, car charger, or conventional electrical outlet, thus suitable for various environments.

Australian Regulations and Safety Standards
AS/NZS Electrical Requirements
In both Australia and New Zealand, electrical installation must comply with the AS/NZS 3000:2018 standard which is also known as the Wiring Rules. It is a standard outline that helps minimize regulatory requirements for safe electrical installation and allows for safety across all applications.
Importance Of RCM
The RCM helps in showing that the electrical product you are using complies with both electrical safety regulations as well as the electromagnetic compatibility that is required in Australia and New Zealand. Moreover, products that have the RCM mark also show that they follow the standards of AS/NZS 4417, confirming that they all meet the safety and functionality criteria.
MEPS Regulations
Australia also uses Minimum Energy Performance Standards which are used to showcase energy efficiency in electrical appliances. In addition to this, these regulations also set mandatory performance criteria that the product must meet and aims to reduce energy consumption along with environmental impact. Also, following the MEPS is crucial for manufacturers and suppliers for them to legally sell their product in the Australian Market.
FAQs
Can I power my home using DC power?
While most Australian homes only have AC power supplies, you can use DC systems by using solar panels or battery storage.
Feasibility of installing DC fast chargers at home
Even though installing a DC fast charger at home is possible, you just have to make sure that you have the proper electrical infrastructure and the cost can vary depending on the charger, capacity, installation process, etc.
Is it safe to use my battery charger as a DC power supplier?
Absolutely, you can use your battery charger to provide DC power but make sure that it matches the voltage and current requirement of the device.
Are there any potential impacts of DC-DC chargers on my battery's health?
A DC-DC charger helps regulate charging, which allows it to prevent overcharging and further increases the lifespan of the battery if it is managed properly.
What is the easiest way to get or create DC power domestically?
You can get DC power by using solar panels, batteries or an AC-DC power converter.
Are there any risks and consequences of using an incorrect power type?
If you use an incompatible power type, it can damage your device, leading to inefficiency or even electrical hazards.
Are there any operational limits and continuous operation guidelines for using a DC motor?
Your DC motors require proper voltage, cooling and maintenance to make sure that your device has safe and long-term operation.
Maintenance and Best Practices
Regularly maintaining your DC power will aid in its safety and longevity. The best way to do this is by checking your voltage stability, checking any wiring damage, cleaning the components to prevent any dust buildup and making sure that it is in a properly ventilated area. Plus, routine testing and compliance with safety standards can also aid in maintaining its effect and prevent any electrical hazards.