Recently, we have witnessed a significant surge in the popularity and acceptance of electric cars (EVs). The technological advancements and their eco-friendly nature have made the masses opt for them more each day.
The world continues to embrace sustainable solutions, and one of the solutions is using electric vehicles and renewable energy such as solar and wind. Using EVs reduces carbon emissions, which aims to combat climate change.
The appeal of electric vehicles lies in their tons of benefits, such as low operating costs, reduced dependency on fossil fuels by harnessing the use of electricity and other sustainable sources of energy, promotes efficiency, and several environmental benefits.
However, although packed with many benefits, EVs have their own share of challenges. Some of the challenges with EVs include long charging hours, limited driving range, and inadequate infrastructure development. The automakers and the stakeholders at large are working to overcome these challenges.
In this article, we shall delve into the world of electric cars in Australia, the aspect of ownership, the costs of charging, and financial and other considerations. Keep on reading.
The Basic Process of Electric Vehicle Charging
The charging process of an electric vehicle is simple to understand. It involves transferring electrical energy from an outlet to the battery of an EV to recharge. The following is a breakdown of the process:
1. Plug-In
Start by connecting an EV to a charging station with a charging cable. The cable has two ends; for plugging into the charging station on one end and into the EV on the other.
2. Authentication and Communication
The EV and charging station will authenticate to establish a connection and verify the credentials of the EV. This is to ensure the charging station and the EV are compatible and for authorization of the charging session.
3. Power Conversion
The charging station converts the AC (alternating current) from the power grid to DC (direct current) for efficient charging of the battery. The conversion is crucial since most electric vehicles utilize DC batteries while most power stations supply power in AC.
4. The Charging Modes
Most EVs have varied charging modes depending on battery capabilities and equipment. The modes are categorized into:
- Level 1
Utilizes a standard household outlet (120V AC) with a slow charging rate- approximately 2-5 miles of range per hour.
- Level 2
Has a faster charging rate at a higher-powered charging station (240V AC), with approximately 10-30 miles of range per hour.
- Level 3
Commonly known as DC Fast Charging (DCFC). It is a fast charging level employing high-power charging stations supplying DC power to the battery of the EV. Provides a high amount of charge within a short period, approximately 20-30 minutes or 60-80 miles of range.
5. The Charging Process
The charging session starts, and electricity flows from the charging station to the EVs battery using a charging cable. The EV has an onboard charger that manages the charging process while monitoring the state of charge, temperature and voltage to ensure efficient and safe charging.
6. Completion
The charging process is complete when the EVs battery is fully charged. Some charging stations provide notifications or signal the completion of the charging session.
Introduction to Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment and Technology

There are several types of electric vehicle charging technologies and equipment available. Here are a few of them:
1. Charging Stations
Also known as Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE), are systems for charging electric vehicles. The EVSE provides physical connection, power conversion and communication for the charging process. The charging stations are usually installed in public, residential areas, and workplaces. However, some stations are portable.
2. The Charging Cable
The charging cable physically connects the charging station to the EV's battery. The cables are available in different lengths and connectors to fit into the EV's charging port and the charging station's outlet.
3. The Onboard Chargers
EVs have an onboard charger to convert AC power into DC power. Also, the onboard charger manages the charging process, ensures safe charging, and monitors the status of the battery.
4. The Plug Types
There are various plugs for EV charging based on regions and countries. Common plugs are Type 1 (J1772), Type 2 (Mennekes), Combined Charging System (CCS), CHAdeMO, and the proprietary Supercharger connector by Telsa.
5. Wireless Charging
The wireless charging technology enables electric vehicles to charge without charging cables. The technology uses electromagnetic induction or resonance to transmit power from the charging pad placed on the ground to the receiver pad installed under the electric car. Wireless charging is still evolving and not as popular.
Factors Influencing the Charging Time and Battery Life
Numerous factors influence the charging time and the battery life of an EV. Here are the major factors:
1. The EV's Battery Capacity
The EV's battery pack is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), and its size affects the charging time. A larger battery takes longer to charge compared to a smaller battery.
2. The Charging Power
The charging power of an EV battery is measured in kilowatts (kW), and it determines the charge rate. The higher charging power enables faster charging. Additionally, the charging power largely depends on the charging equipment and the EV's onboard charger capacity.
3. The State of Charge(SoC)
The current charge level of the battery, also known as the State of Charge, affects the charging time. The EV's battery charges faster when it's at low SoC. When the battery nears the full charge capacity, the charging speed reduces to protect the health of the battery.
4. External Temperatures
Extreme cold or hot temperatures influence the charging time. High temperatures reduce the charging efficiency, while low temperatures increase the charging duration due to numbed chemical reactions in the battery.
5. Battery Management Systems (BMS)
The EV's BMS regulates the charging process, thus optimizing the battery's safety, performance, and lifecycle. BMS monitors and regulates aspects such as the voltage, the charging current, and the temperature ensuring the battery is charging within the safety parameters.
6. Battery Degradation
The EV's battery's performance and capacity may start to degrade. Poor charging habits, such as frequently charging or fully discharging, accelerate the quick degradation of the battery. Safe charging practices for healthy and durable batteries include avoiding extreme temperatures and high charge levels.
Generally, the battery life and charging duration varies depending on the battery chemistry, the model of the EV, and the charging infrastructure. Electric vehicle manufacturers have guidelines and recommendations for efficient charging and how to maximize the battery's durability.
The Cost of Home Charging Electric Vehicles in Australia

The costs of charging an electric vehicle vary across Australia depending on factors such as electricity rates, the charging speed, the size of the battery, and the time of the day the EV is charging. Here's a breakdown of these factors:
1. The Electricity Rates
The electricity rates vary in different states and regions in Australia. Also, it varies with different power providers in each state. Residential electricity rates are categorized into various usage tiers, with higher consumption attracting high rates. Charging your EV during off-peak hours will attract lower rates.
2. The Charging Speed and the Size of the Battery
The EV's battery pack and the charging speed may determine the costs of charging the EV at home. Electric cars with bigger batteries require more energy, resulting in high charging costs. Also, a faster charging speed consumes more electricity and is more expensive.
3. Time of Charging
Most electricity providers have time-of-use tariffs. This means the electricity rates are divided into different categories throughout the day. The off-peak rates are divided into various periods throughout the day. Off-peaks are usually during the night, and electricity rates are much lower. You can take advantage and charge your EV at night.
To know the cost of charging your EV at home:
- Determine the energy consumption of your EV in kilowatt-hours, kWh.
- Refer to the vehicle's specifications or contact the manufacturer.
- Multiply the energy consumption (kWh) by rates from your electricity provider per kilowatt-hour.
What Are the Costs of Charging EVs in Public Charging Stations in Australia?
You can find public charging stations for EVs in public places such as in parking lots, shopping centers, and on the roadsides. The cost of charging at a public charging station depends on factors such as the charging infrastructure and the pricing model of the station. Here is the pricing model breakdown:
1. Flat Fee
Some charging stations charge a flat fee for every hour of charging.
2. Time-Based Fee
The time-based fee is another common pricing model in Australia. You are charged based on the duration spent connected to the charger. The pricing model is useful for instances where you don't need a full charge or for slower chargers.
3. Membership or Subscription Pricing Models
Some charging stations offer subscription or membership pricing models, whereby you pay a recurring cost to use their charging infrastructure. Usually, this pricing model offers discounted rates and other benefits to its members
4. Usage-Based Price
Some public charging stations charge depending on your car's energy in kilowatt-hours. You pay the amount your car consumes.
To get the best charging rates, check the pricing information of various charging stations on their mobile applications or websites.
An Example of Analysis of Charging Costs in Australia
Here are examples of analysis of EV charging costs in Australia.
1. Home Charging
If your electric vehicle has a 50 kWh battery and the electricity provider charges you $0.25 per kWh. If you charge your EV from 0% to 100%, you will pay 50 kWh x $0.25 = $12.50.
2. Public Charging
If you use a public charging station with a flat fee of $1 per hour of charging and charge your EV for two hours, you will pay $1/hour x 2 hours = $2. However, note that the amount of power transferred to your EV can vary depending on the battery capacity and the charging speed.
Note: The above scenarios are hypothetical, and the actual rates can differ depending on your location and other factors.
How to Reduce the Charging Cost of Electric Vehicles?
1. Using Solar Energy and Home Energy Storage Systems to Reduce Charging Costs
a) Install Solar Panels
Investing in superior-quality solar panels can help to significantly reduce electric vehicle charging costs. Harnessing solar energy reduces over-reliance on the grid, and it generally lowers the costs of electricity. Here are the top solar panels you should consider installing for generating power to charge your EV.
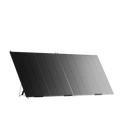
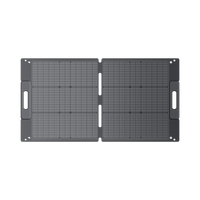
BLUETTI PV200 Solar Panels | 200W

Features
- High Conversion Efficiency
The 200-Watt Monocrystalline solar panel has a high conversion efficiency of 23.4%. It has excellent 95% transparency and performs better than polycrystalline solar panels, even in low-light conditions.
- Durable and Waterproof
The BLUETTI PV200 Solar Panels are equipped with a durable and scratch-resistant ETFE material. The IP65 waterproof material makes it ideal for outdoor activities such as fishing, camping, and hiking. However, do not soak it in water or leave it under rain.
- Versatile
It is equipped with an MC4 connector, and it is compatible with most solar generators such as BLUETTI AC200P, BLUETTI EB3A, BLUETTI EB70, BLUETTI EP500, and power stations.
- Foldable and Portableroducts/ac300-b300
The BLUETTI PV200 solar panel is foldable and lightweight for easy portability. The folded size is 23.4 x 24.8 inches and weighs 16.1 lbs.
Pros
- Lightweight and foldable for easy portability
- Excellent power output
- Solid and durable construction
- Quick and easy setup with three angles
- IP65 certified
Cons
- Has a limited number of USB ports.
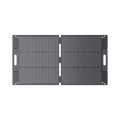
2. BLUETTI PV350 SOLAR PANEL | 350W

Features
- Off-Grid Power Supply
The BLUETTI PV350 solar panel is cost-friendly and highly efficient at harnessing solar energy. The portable solar panels can power different appliances and devices such as mobile phones, fridges, drones, and laptops on the go.
- Foldable and Lightweight for Easy Portability
The foldable size of the solar panel is 35.6 x 24.1 x 2.5 inches and a weight of 30.61 lbs. It is easy to set up and convenient for camping, caravanning, hiking, and other outdoor activities.
- Durable and Waterproof
The solar panel is made with top laminated technology and durable ETFE material, which makes the 350w solar panel highly durable, scratch resistant, high light transmittance, and easy to clean with a wet cloth.
- Conversion Rate of 23.4%
The BLUETTI PV350 is constructed with a 350-Watt monocrystalline solar panel guaranteeing high conversion efficiency of up to 23.4%. The solar panel has an excellent 95% transparency and performs well in low-light conditions. It comes with four fixed stands to maximize panels in direct sunlight.
- Wide Compatibility
The BLUETTI PV350 solar panels are equipped with an MC4 connector compatible with several solar generators such as the BLUETTI AC200P, BLUETTI AC200MAX, BLUETTI AC300, BLUETTI EP500, and BLUETTI EP500 PRO.
2. Taking Advantage of Net Metering
Net metering allows you to maximize your savings and reduce the charging costs of your EV. Net metering enables you to sell excess solar electricity to the grid utility companies. During high sunny periods, you can earn credits to offset your energy consumption when charging your electric vehicle at night and during low solar production seasons.
3. Home Energy Storage System Installation
Consider pairing your solar panels with an efficient energy storage system such as BLUETTI solar battery to reduce further the costs of charging your EV. During the perfect sunny days when the solar panels generate excessive solar power, the excess energy is stored in the battery for future use. You can use the stored energy to charge your electric vehicle, thus effectively reducing reliance on grid power and electricity costs. The home battery backup you should invest in is the
BLUETTI AC200MAX + B230 | Home Battery Backup
Features
- High Capacity
The portable BLUETTI AC200MAX has a high continuous load of 2200W, with a high capacity 2048 Wh LiFePO4 battery. You can easily control the power station through a mobile application.
- Expandable Power
The power station is equipped with a 2048 Wh LifePO4 battery. The user can triple the capacity to 6,144Wh using 2x BLUETTI B230 batteries or quadruple to 8,192Wh using 2x BLUETTI B300 batteries. The power is sufficient for powering your home, coffee makers, refrigerators, lighting, CPAP equipment, air conditioner, electric kettles and charging devices.
- Several Outputs
The BLUETTI AC200 MAX has several outputs, including Wireless charging (15W), 4x 230 V outputs, USB-A, USB-C PD (100 W), and a 12V - 30A. You can use the power station at home during outages, on the caravan, motorhome and on boats.
- Charging Via Solar Panels
The BLUETTI AC200MAX can be fully charged with 900 Watts. Also, you can use the adapter to charge the station with 1400 watts, which can be fully charged in 2 hours. You can use the BLUETTI mobile app to monitor the status of the battery and charging options.
4. Using Off-Peak Time Charging to Reduce Charging Costs
- Time-of-Use (TOU) Tariffs
Utility companies have time-of-use tariffs, whereby the electricity rates vary during different times of the day. During off-peak hours, the electricity costs are lower than peak hours when the demand is high. Understand the TOU tariff to identify the off-peak window frame to reduce costs.
- Charge During Off-Peak Hours
Charging your EV during off-peak hours, such as late nights or early mornings, can significantly reduce the charging costs. Consider using programmable charging features and smart charging systems to allow you to schedule charging sessions during off-peak time.
- Discover Incentives for Off-Peak Charging
Some utility companies provide incentives or discounts for charging your EV during off-peak hours. These discounts and incentives help to significantly reduce the costs of charging your electric car.
5. Selecting a Suitable Public Charging Network to Reduce Charging Costs
- Research the Charging Network Providers
Research various charging network providers around you. Compare the pricing, per kilowatt-hour rates, and subscription fees to identify the most cost-effective charging station. Also, look out for stations with regular discounted rates.
- Consider Membership Programs
Most charging networks have membership programs providing access to discounted charging rates. Check out the programs that match your charging needs and driving habits.
- Use Charging Station Apps
Utilize the charging stations' locator and apps to get real-time information on the charging stations' location, availability and pricing. It enables you to identify the most affordable charging options and plan your routes, thus optimizing the charging costs.
Final Thoughts
Electric vehicles have a promising future in the transport industry. They are easy to maintain, and zero emissions are great for the environment and the efforts to reverse climate change. The factors affecting the cost of charging EVs in Australia are the electricity rates, the charging infrastructure, the battery capacity, and the charging speed, among others.
The benefits of electric vehicles are long-term fuel cost savings, longer vehicle lifespan, tax incentives and rebates, reduced maintenance costs, and environmental and health benefits.
The prospect of electric vehicles is bright with technological advancements in battery charging technology, cost reductions, the expansion of charging infrastructure, supportive government policies, and the integration with different energy sources, such as solar power.





































































![[Phased Out] BLUETTI B80P Expansion Battery | 806Wh](http://www.bluettipower.com.au/cdn/shop/files/202310025B80P_2000-2000px_4_4caa0c1c-4dab-4272-9e9b-2b7507e5bd81.jpg?v=1713777870&width=200)
![[Phased Out] BLUETTI B210P Expansion Battery | 2,150Wh](http://www.bluettipower.com.au/cdn/shop/files/2_08cf9ef3-03a4-4489-b641-d3edb8094896.webp?v=1716016566&width=200)















































































































![[Phased Out] BLUETTI B80P Expansion Battery | 806Wh](http://www.bluettipower.com.au/cdn/shop/files/202310025B80P_2000-2000px_4_4caa0c1c-4dab-4272-9e9b-2b7507e5bd81.jpg?v=1713777870&width=120)
![[Phased Out] BLUETTI B210P Expansion Battery | 2,150Wh](http://www.bluettipower.com.au/cdn/shop/files/2_08cf9ef3-03a4-4489-b641-d3edb8094896.webp?v=1716016566&width=120)